FTP, or File Transfer Protocol, is a standard network protocol used to transfer files between a client and a server on a computer network. It facilitates the seamless exchange of files over the internet or an intranet. FTP operates on a client-server model, where the client initiates a connection to the server to upload or download files.
Numerous FTP servers cater to diverse needs. vsftpd, known for its security focus, is lightweight and efficient. FileZilla Server offers a user-friendly interface and compatibility with Windows. Additionally, popular cloud services like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure provide FTP capabilities.
In this post, we will be setting up vsftpd for a directory on Raspberry Pi.
PermalinkPrerequisites
Access to Raspberry Pi with
sudoprivilegesRaspberry Pi connected to the same network as your local machine. More information can be found here.
PermalinkPreparing dedicated folder for FTP
First, in the Raspberry Pi we’ll create the directory where we plan to host the files:
sudo mkdir /home/<USER>/ftp
Secondly, we configure the permissions for the directory:
sudo chown nobody:nogroup /home/<USER>/ftp
Next, we remove write permissions:
sudo chmod a-w /home/<USER>/ftp
Following that, we create the directory for file uploads:
sudo mkdir /home/<USER>/ftp/files
Then assign ownership to that folder:
sudo chown <USER>:<USER> /home/<USER>/ftp/files
Lastly, we create a test file:
echo "test file" | sudo tee /home/<USER>/ftp/files/test.txt
PermalinkConfigure vsftpd
The configuration file is located at /etc/vsftpd.conf
We'll begin by confirming the following settings:
anonymous_enable=NO
local_enable=YES
These settings prevent anonymous logins and permit local logins, respectively. Keep in mind that enabling local logins means that any normal user listed in the /etc/passwd file can be used to log in.
In addition to these, we'll also modify few settings:
write_enable=YES
chroot_local_user=YES
These settings allow users to add, change, or remove files and directories on the file system and prevent user from accessing any files or commands outside the directory tree, respectively.
Lastly, we'll add the following settings:
user_sub_token=$USER
local_root=/home/$USER/ftp
This setup ensures that the configuration will allow for this user and future users to be routed to the appropriate user’s home directory when logging in.
PermalinkReload vsftpd
Once the configuration file has been modified and saved, run the following command to restart vsftp daemon:
sudo systemctl restart vsftpd
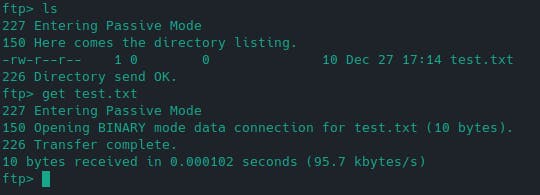
PermalinkTesting FTP connection
From your local machine, run the following commands:
ftp -p <IP ADDRESS OF RASPBERRY PI>
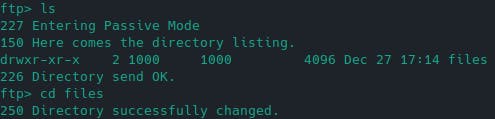
ftp> cd files
ftp> get test.txt